Matrix Factorization
A Novel Variational Form of the Schatten-p Quasi-Norm
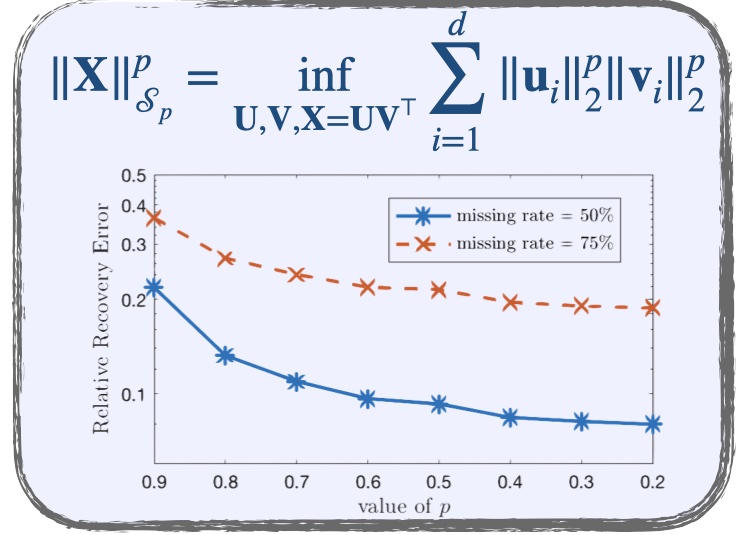
In this work we aim to reduce the high computational cost induced by Schatten-p quasi-norm minimization, variational forms, which are defined over smaller-size matrix factors whose product equals the original matrix, have been proposed. Here, we propose and analyze a novel variational form of Schatten-p quasi-norm which, for the first time in the literature, is defined for any continuous value of p ∈ (0, 1] and decouples along the columns of the factorized matrices. The proposed form can be considered as the natural generalization of the well-known variational form of the nuclear norm to the nonconvex case i.e., for p ∈ (0, 1). Notably, low-rankness is now imposed via a group-sparsity promoting regularizer. The resulting formulation gives way to SVD-free algorithms thus offering lower computational complexity than the one that is induced by the original definition of the Schatten-p quasi-norm. A local optimality analysis is provided which shows that we can arrive at a local minimum of the original Schatten-p quasi-norm problem by reaching a local minimum of the matrix factorization based surrogate problem. In addition, for the case of the squared Frobenius loss with linear operators obeying the restricted isometry property (RIP), a rank-one update scheme is proposed, which offers a way to escape poor local minima.
[1] Paris Giampouras, René Vidal, Athanasios Rontogiannis, Benjamin Haeffele, “A novel variational form of the Schatten-p quasi-norm”, NeurIPS, 2020.